A processed food designed for infants, typically featuring a blend of various fruit flavors, is commonly categorized as a ‘mixed fruit’ variety within the realm of commercially prepared products for babies. These often incorporate fruits such as apples, bananas, peaches, and pears, pureed to achieve a smooth consistency suitable for early consumption. The combinations aim to provide a range of vitamins and nutrients in a palatable format for developing palates.
The inclusion of multiple fruit types offers a diverse nutritional profile, contributing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, beneficial for infant development and digestive health. Historically, the introduction of these homogenized fruit blends provided a convenient and accessible option for parents, particularly in urban settings where fresh fruit availability or preparation time was limited. These offerings often present a more consistent and predictable taste compared to individual fruits, potentially aiding in acceptance by young children during the weaning process.
The following sections will delve into the nutritional composition, preparation methods, potential advantages, and possible considerations when selecting a fruit-based food product for infant consumption.
Considerations When Incorporating Fruit Blends into an Infant’s Diet
The subsequent guidelines offer informed suggestions regarding the integration of mixed fruit purees into an infant’s nutritional plan.
Tip 1: Prioritize Ingredient Transparency: Thoroughly examine the product label to ensure a comprehensive understanding of all components. Scrutinize for the presence of added sugars, artificial preservatives, or other non-essential ingredients. Opt for varieties with minimal additives.
Tip 2: Introduce One Flavor at a Time Initially: When introducing new foods, it is advisable to start with single-ingredient purees before progressing to combinations. This strategy facilitates the identification of potential allergies or sensitivities to specific fruits within the blend.
Tip 3: Monitor for Allergic Reactions: Closely observe the infant for any indications of an allergic response, such as skin rashes, digestive discomfort, or respiratory distress, particularly after the initial introduction of a new fruit blend. Consult a pediatrician if any adverse reactions are suspected.
Tip 4: Emphasize Homemade Options When Feasible: Preparing fruit purees at home provides greater control over ingredient selection and processing methods. Steam or bake fruits to retain nutrients, and blend to a smooth consistency appropriate for the infant’s developmental stage.
Tip 5: Adhere to Age-Appropriate Textures: As the infant progresses through developmental stages, gradually adjust the texture of the fruit puree to encourage oral motor skills and acceptance of more complex food consistencies. Start with smooth purees and transition to slightly thicker textures.
Tip 6: Maintain Proper Hygiene Practices: Adhere to strict hygiene protocols during food preparation and storage to minimize the risk of contamination. Wash hands thoroughly before handling food, and use clean utensils and storage containers. Store opened containers in the refrigerator and consume within the recommended timeframe.
Tip 7: Avoid Over-reliance on Fruit Purees: While these fruit combinations can provide essential nutrients, ensure a balanced diet encompassing a variety of food groups, including vegetables, proteins, and grains. Fruit purees should complement, not replace, other essential components of a healthy diet.
The prudent application of these recommendations can assist caregivers in making informed decisions regarding the selection and integration of processed fruit blends into an infant’s dietary regime, promoting optimal health and well-being.
The subsequent section will address potential drawbacks associated with the exclusive or excessive consumption of these processed food items.
1. Nutritional Content
The nutritional content of commercially prepared fruit blends for infants, a specific category often described using the key word phrase, directly impacts infant growth and development. Cause-and-effect relationships are evident, wherein insufficient or imbalanced nutritional profiles can lead to deficiencies, affecting physical and cognitive milestones. Consequently, appropriate levels of vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber become essential components. For example, a product lacking sufficient vitamin C could compromise immune system development, while inadequate fiber could contribute to digestive irregularities.
A practical consideration involves assessing the labels of marketed products to determine the actual nutritional values provided. Certain brands may emphasize specific vitamins or minerals, while others might prioritize affordability, potentially compromising nutritional density. The sourcing of ingredients plays a critical role, with organic produce possibly offering reduced exposure to pesticides, albeit not always guaranteeing superior nutritional content. Furthermore, the processing methods employed can either preserve or degrade certain nutrients, influencing the overall nutritional value of the end product.
In summary, the nutritional content represents a vital factor when selecting a commercially available fruit blend for infant consumption. Challenges remain in consistently ensuring optimal nutritional profiles across all product lines, requiring both parental diligence in label review and ongoing efforts from manufacturers to prioritize nutrient preservation. Understanding this connection allows for more informed choices that support healthy infant development.
2. Ingredient Sourcing
Ingredient sourcing represents a foundational element in the production of fruit-based infant comestibles, significantly impacting product quality, safety, and nutritional value. The origin and handling of raw materials directly influence the final characteristics of the product, potentially affecting infant health and well-being.
- Geographic Origin and Climate
The geographic location where fruits are grown and the prevailing climate conditions exert considerable influence on their nutritional composition and flavor profile. Fruits cultivated in regions with optimal sunlight, rainfall, and soil conditions often exhibit superior vitamin and mineral content compared to those grown in less favorable environments. Understanding the geographic origin allows for assessment of potential environmental contaminants present in the growing region, informing quality control protocols.
- Agricultural Practices
Agricultural practices, including the use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, directly affect the chemical residue levels in raw fruits. Organic farming practices, which eschew synthetic chemicals, aim to minimize exposure to potentially harmful substances. However, even organically grown produce may be subject to environmental contamination. Verification of agricultural practices through certifications and supplier audits becomes crucial in ensuring ingredient integrity.
- Transportation and Storage
The conditions under which fruits are transported and stored from the farm to the processing facility significantly impact their freshness and nutritional value. Prolonged storage or inadequate temperature control can lead to spoilage, nutrient degradation, and increased risk of microbial contamination. Implementation of cold chain management and rapid transit protocols helps preserve the quality of raw materials.
- Supplier Relationships and Traceability
Establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers is essential for ensuring consistent ingredient quality and traceability. Comprehensive documentation of the entire supply chain, from farm to processing facility, enables rapid identification and isolation of contaminated batches in the event of a product recall. Transparent supplier relationships foster accountability and promote ethical sourcing practices.
The multifaceted nature of ingredient sourcing necessitates a rigorous and systematic approach to procurement and quality control. A comprehensive understanding of geographic origins, agricultural practices, transportation logistics, and supplier relationships allows manufacturers to produce safe and nutritious fruit-based infant food products that meet stringent quality standards. Prioritizing ingredient sourcing enhances consumer confidence and promotes infant health.
3. Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of fruit-based products for infants directly impacts the final product’s safety, nutritional integrity, and consumer acceptance. Cause-and-effect relationships are readily apparent: the choice of processing techniques influences nutrient retention, while sanitation protocols determine the presence of harmful microorganisms. The process serves as a critical component of this product category because it transforms raw ingredients into a form suitable for infant consumption, preserving them for extended shelf life, and ensuring consistent texture and flavor. For instance, flash pasteurization, used to eliminate pathogens, also minimizes heat damage to heat-sensitive vitamins compared to traditional canning methods. Similarly, aseptic packaging techniques protect the product from contamination without requiring the addition of preservatives.
Different manufacturing approaches offer varying advantages and disadvantages. Hydrostatic pressure processing, for example, can inactivate bacteria while preserving the natural color and flavor of fruits, but the equipment and operational costs may be higher. Mechanical pureeing, followed by vacuum concentration, can concentrate the fruit solids while minimizing thermal damage, but requires careful monitoring to prevent enzymatic browning and flavor degradation. The specific choice of process is influenced by factors such as the desired shelf life, the fruit variety being processed, and cost considerations. Furthermore, adherence to strict quality control measures, including regular testing for microbial contamination, pesticide residues, and heavy metals, is essential to ensure product safety.
In summary, the manufacturing process plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and safety of blended fruit products intended for infants. By understanding the intricacies of each step, from ingredient preparation to packaging, manufacturers can optimize their operations to deliver nutritionally sound and safe food options for this vulnerable population. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing the need for effective preservation with the desire to retain the inherent goodness of fresh fruits, while maintaining cost-effectiveness and meeting stringent regulatory requirements.
4. Texture Consistency
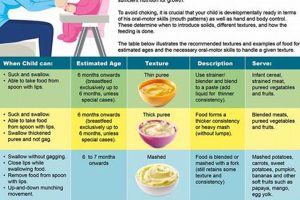
Texture consistency plays a paramount role in the realm of commercially prepared fruit blends for infants. It is a critical factor influencing not only product acceptance but also, and more importantly, developmental readiness and safety. The consistency of these products must align with an infant’s evolving oral motor skills to facilitate safe swallowing and prevent choking hazards.
- Developmental Stage Alignment
Infants progress through distinct developmental stages, each characterized by specific oral motor capabilities. Stage 1 purees, typically introduced around six months, necessitate an extremely smooth, lump-free consistency due to the infant’s limited ability to manage textured foods. As infants advance, Stage 2 and Stage 3 foods may incorporate slightly thicker consistencies and small, soft pieces to encourage chewing and oral motor skill development. Incongruence between food texture and developmental stage can lead to rejection of the food, feeding difficulties, or an increased risk of aspiration.
- Swallowing Safety and Aspiration Risk
The viscosity and particle size distribution of fruit blends directly impact swallowing safety. A product that is too thin may be difficult for an infant to control in the mouth, leading to premature swallow initiation and potential aspiration. Conversely, a product with large or hard particles poses a choking hazard. Manufacturers implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure texture consistency meets established safety standards, often employing techniques such as sieving, homogenization, and viscosity measurements to maintain uniformity and minimize the risk of aspiration.
- Sensory Acceptance and Palatability
Texture plays a significant role in sensory acceptance and palatability, influencing an infant’s willingness to consume the product. Overly grainy, lumpy, or viscous textures can be unappealing, leading to food refusal. Conversely, a smooth, homogenous texture is generally well-accepted by infants. Product development teams often conduct sensory evaluations to optimize texture characteristics, ensuring palatability without compromising safety or nutritional value.
- Manufacturing Variability and Quality Control
Maintaining consistent texture across different batches of fruit blends presents a significant manufacturing challenge. Variations in fruit ripeness, processing parameters, and storage conditions can affect the final texture. To mitigate these variations, manufacturers implement stringent quality control measures, including in-process texture analysis, regular equipment calibration, and comprehensive ingredient specifications. These measures aim to minimize batch-to-batch variability and ensure that the texture consistently meets established standards.
Therefore, texture consistency, in the context of infant fruit blends, is not merely an aesthetic attribute but a crucial determinant of safety, developmental appropriateness, and product acceptance. The interplay of developmental stage alignment, swallowing safety, sensory acceptance, and manufacturing variability underscores the importance of rigorous quality control measures and informed product formulation to ensure the well-being of the target consumer.
5. Storage Stability
Storage stability, defined as the ability of a product to maintain its intended characteristics (nutritional value, safety, sensory attributes) over a defined period under specified storage conditions, is a critical factor for commercially produced fruit blends for infants. Poor storage stability can lead to spoilage, nutrient degradation, development of off-flavors, and increased risk of microbial contamination, rendering the product unsuitable for consumption. The effectiveness of preservation techniques used during manufacturing directly influences storage stability. For example, if proper sterilization procedures are not followed, bacterial growth may occur, leading to gas production and bulging of the packaging within a short timeframe, compromising product safety. A manufacturer employing subpar packaging materials may witness increased oxygen permeability, resulting in oxidation of vitamins, particularly vitamin C, thereby diminishing the product’s nutritional profile. Furthermore, improper storage temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions, causing changes in color, texture, and flavor, impacting consumer acceptance.
The implementation of specific preservation methods is directly linked to enhanced storage stability. Aseptic processing, combined with hermetically sealed packaging, effectively eliminates viable microorganisms, thereby extending shelf life without the need for excessive heat treatment. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) can further enhance storage stability by reducing oxygen levels within the package, inhibiting enzymatic browning and retarding the growth of spoilage organisms. The use of appropriate packaging materials, such as multi-layered films with barrier properties, prevents moisture and oxygen ingress, preserving product quality. Additionally, stringent quality control measures, including regular testing for microbial contamination, pH levels, and sensory attributes, provide ongoing verification of storage stability. Real-world examples include baby food products that, under proper storage conditions (e.g., refrigeration after opening), maintain their quality attributes and remain safe for consumption within the manufacturer-specified timeframe, ensuring infants receive the intended nutritional benefits.
In summary, storage stability represents a vital component in the production and distribution of fruit-based comestibles for infants. While effective preservation methods, packaging strategies, and quality control measures contribute significantly to maximizing storage stability, challenges persist in maintaining product quality throughout the distribution chain and in the consumer’s home. The ability to consistently achieve and demonstrate storage stability directly impacts product safety, consumer confidence, and the overall nutritional contribution of the food item to infant health and development.
6. Market Availability
Market availability significantly influences consumer access to specific infant food products. Its role extends beyond mere physical presence on shelves; it encompasses factors affecting procurement ease, geographical distribution, and affordability, all impacting parents’ ability to provide their infants with particular nutritional options.
- Geographic Distribution and Retail Channels
The geographical distribution of fruit blend products, including the type mentioned, dictates accessibility for different populations. Products widely available in urban centers may be scarce in rural areas, creating disparities in nutritional opportunities. Retail channels, such as supermarkets, specialty stores, and online vendors, further influence availability. Limited distribution through specific retailers can restrict consumer choice and increase product costs, particularly in regions with fewer shopping options.
- Brand Diversity and Product Range
The diversity of brands offering fruit combinations and the breadth of their product ranges significantly influence consumer choice. A market dominated by a few major brands may offer limited flavor profiles or nutritional variations. Conversely, a market with numerous smaller brands can introduce greater innovation and tailored options but might also present challenges in terms of consistency and quality control. The availability of organic or allergen-free options also falls under this facet, catering to specific dietary needs and preferences.
- Pricing and Affordability
Pricing dynamics and product affordability directly impact consumer purchasing power. High-priced fruit blends may be inaccessible to low-income families, creating nutritional inequities. Market competition and promotional activities influence price fluctuations, affecting purchase decisions. Government subsidies or nutritional assistance programs can mitigate these financial barriers, expanding access for vulnerable populations.
- Regulatory Approvals and Product Recalls
Regulatory approvals and instances of product recalls directly influence product availability and consumer confidence. Products undergoing regulatory scrutiny or subject to recalls may be temporarily or permanently removed from the market, limiting consumer choice and raising concerns about product safety. Transparent labeling practices and adherence to quality control standards enhance consumer trust and ensure the continued availability of safe and reliable infant food options.
These components collectively determine the extent to which a particular product, including blended fruit purees, is accessible to diverse consumer segments. Addressing disparities in market availability requires a multifaceted approach encompassing strategic distribution networks, competitive pricing strategies, transparent regulatory oversight, and effective consumer education to ensure equitable access to nutritious food for all infants.
7. Regulatory Standards
Regulatory standards are crucial in ensuring the safety, quality, and nutritional adequacy of commercially produced food designed for infants, including fruit blends. These standards are established by governmental bodies and international organizations to protect this vulnerable population from potential health hazards and deceptive marketing practices.
- Microbiological Safety Standards
Microbiological safety standards dictate acceptable levels of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in infant food products. These standards are implemented to prevent foodborne illnesses that can have severe consequences for infants due to their underdeveloped immune systems. Stringent testing protocols and manufacturing practices, such as sterilization and pasteurization, are required to meet these standards. For example, the presence of Clostridium botulinum in baby food, even in minute quantities, can be life-threatening, necessitating rigorous adherence to sterilization guidelines during production. The absence of such standards or lax enforcement could lead to widespread contamination and significant public health crises.
- Pesticide Residue Limits
Pesticide residue limits specify the maximum permissible levels of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables used in infant foods. Infants are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of pesticides due to their smaller body mass and developing organ systems. Regulatory bodies establish these limits based on comprehensive risk assessments to minimize pesticide exposure. Compliance requires meticulous sourcing of raw materials from growers adhering to sustainable agricultural practices and rigorous testing of finished products. Failure to adhere to these limits can expose infants to neurotoxic effects and other health risks associated with pesticide exposure, warranting stringent monitoring and enforcement.
- Nutritional Content Requirements
Nutritional content requirements define the minimum and maximum levels of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients, in infant food products. These requirements are designed to ensure that infants receive adequate nutrition for optimal growth and development. Regulatory bodies establish these standards based on scientific research and dietary recommendations. Compliance necessitates careful formulation and processing to preserve nutrient content. For example, the addition of vitamin C to fruit blends enhances iron absorption, while the careful selection of fruits ensures a balanced profile of vitamins and minerals. Non-compliance can lead to nutritional deficiencies, impacting infant health and cognitive development.
- Labeling Regulations
Labeling regulations mandate accurate and transparent labeling of infant food products, providing consumers with essential information about ingredients, nutritional content, potential allergens, and safe handling instructions. These regulations aim to empower parents to make informed choices about the foods they feed their infants. Clear and concise labeling helps prevent accidental exposure to allergens and facilitates the identification of products suitable for specific dietary needs. For example, the listing of added sugars and artificial sweeteners enables parents to avoid products with potentially harmful additives. Non-compliance can mislead consumers, increasing the risk of allergic reactions or inappropriate dietary choices.
These facets of regulatory standards collectively shape the safety, nutritional quality, and consumer accessibility of fruit blends produced for infant consumption. Adherence to these standards, coupled with rigorous enforcement, is vital for safeguarding infant health and fostering consumer confidence in the safety and integrity of these products.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, usage, and nutritional aspects of processed fruit blends for infants. The information provided is intended to offer clarity and guidance for caregivers.
Question 1: Are fruit blends a nutritionally complete food for infants?
No, fruit blends should not serve as the sole source of nutrition for infants. While they provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber, they lack essential proteins and fats required for optimal growth and development. A balanced diet encompassing a variety of food groups, including vegetables, grains, and proteins, is necessary to meet an infant’s complete nutritional needs.
Question 2: What is the recommended age for introducing fruit blends to infants?
The recommended age for introducing solid foods, including fruit blends, is generally around six months. Before this age, breast milk or formula should be the primary source of nutrition. Prior to introducing solids, consult with a pediatrician to assess developmental readiness and identify any potential allergies or sensitivities.
Question 3: How can potential allergic reactions to fruit blends be identified?
Introduce single-ingredient fruit purees before offering blends to identify potential allergens. Monitor the infant for signs of an allergic reaction, such as skin rashes, hives, digestive upset, or respiratory distress. If any adverse reactions occur, discontinue use and consult a pediatrician or allergist for evaluation.
Question 4: Are organic fruit blends nutritionally superior to non-organic options?
Organic fruit blends are produced without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which may reduce exposure to potentially harmful chemicals. However, there is limited evidence to suggest that organic options are consistently nutritionally superior to non-organic alternatives. Choose products based on ingredient quality, nutritional content, and adherence to safety standards, regardless of organic certification.
Question 5: What precautions should be taken regarding the storage and handling of opened fruit blend containers?
Opened containers of fruit blends should be refrigerated promptly and consumed within the manufacturer’s recommended timeframe, typically 24-48 hours. Always use clean utensils when serving and discard any uneaten portions to prevent bacterial contamination. Examine the container for signs of spoilage, such as bulging lids or an off odor, before serving.
Question 6: Is homemade fruit puree preferable to commercially prepared blends?
Homemade fruit puree allows for greater control over ingredients and processing methods, potentially minimizing additives and preservatives. However, commercially prepared blends often undergo rigorous quality control and testing to ensure safety and nutritional adequacy. Both options can be suitable, provided that appropriate safety measures are followed during preparation and storage.
In summary, incorporating fruit blends into an infant’s diet requires careful consideration of nutritional needs, age-appropriateness, potential allergies, and proper storage practices. Informed decision-making can contribute to the healthy growth and development of infants.
The subsequent section will delve into potential advantages and disadvantages associated with exclusive reliance on processed fruit-based infant food products.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding exploration of “tutti frutti baby food” and related infant fruit products has underscored several critical facets. Nutritional content, ingredient sourcing, manufacturing processes, and adherence to stringent regulatory standards all play pivotal roles in determining the safety and nutritional value of these offerings. Market availability and informed consumer choices further influence the role these products play in infant diets. The key takeaway is that “tutti frutti baby food” is but one component of a complex landscape influencing infant health.
Ongoing diligence in research, manufacturing practices, and regulatory oversight is paramount. Continued examination of the long-term effects of processed food on infant health, coupled with a commitment to transparent labeling and ethical marketing practices, is essential. Parents and caregivers should remain vigilant in making informed decisions, consulting with healthcare professionals to ensure optimal infant nutrition and development. The significance of this topic necessitates ongoing commitment to safety, quality, and responsible consumer guidance.