Processed and packaged comestibles designed specifically for infants and toddlers, frequently sold in sealed glass containers, offer a convenient and readily available option for introducing solid foods to a developing diet. These prepared meals encompass a variety of single-ingredient purees and more complex blends, catering to diverse nutritional requirements and stages of development. Examples include vegetable blends, fruit purees, and meat-based preparations.
The accessibility and ease of use afforded by commercially prepared infant nourishment contributes significantly to modern childcare. It provides a practical solution for caregivers managing busy schedules and ensures consistent nutritional intake. Historically, the development of these products represented a significant advancement in infant feeding practices, offering improved hygiene and standardization compared to earlier methods. The presence of these items addresses diverse dietary requirements and ensures a degree of predictability in nutritional composition.
The ensuing discussion will delve into the composition, manufacturing processes, nutritional considerations, and potential advantages associated with this type of infant feeding solution. The exploration will further examine labeling requirements, safety protocols, and consumer guidance related to its use.
Guidance for Utilizing Prepared Infant Meals
The following provides informative guidance for caregivers who choose to incorporate commercially prepared infant meals into a child’s dietary regimen. Careful consideration of these points can contribute to informed and responsible feeding practices.
Tip 1: Prioritize Stage-Appropriate Varieties: Select products formulated for the child’s developmental stage, as indicated on the packaging. Formulations for earlier stages typically feature smoother consistencies and simpler ingredient lists, while later-stage options may include chunkier textures and more complex flavor combinations.
Tip 2: Scrutinize Ingredient Lists: Thoroughly examine the ingredient list before purchase. Opt for products with minimal additives, preservatives, and added sugars or salts. Prioritize options featuring recognizable whole foods.
Tip 3: Adhere to Storage Guidelines: Strictly follow the storage instructions provided on the packaging. Refrigerate opened containers promptly and discard any unused portions after the recommended timeframe to minimize the risk of bacterial contamination.
Tip 4: Practice Safe Feeding Techniques: Utilize a clean spoon for each feeding and avoid directly feeding from the container. This helps prevent the introduction of saliva and potential spoilage of the remaining product.
Tip 5: Observe for Allergic Reactions: Introduce new varieties one at a time, allowing several days between each introduction. This enables caregivers to effectively monitor for any potential allergic reactions or sensitivities.
Tip 6: Evaluate Product Appearance and Odor: Prior to feeding, carefully inspect the contents for any signs of spoilage, such as unusual odors, discoloration, or separation. Discard any product that exhibits such characteristics.
Tip 7: Understand Heating Recommendations: If warming is desired, follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid microwaving in the container. Transfer the contents to a microwave-safe dish and ensure even heating to prevent hot spots.
The careful adherence to these guidelines promotes both the safety and nutritional well-being of the infant. Informed selection and responsible usage are paramount when incorporating these products into a child’s diet.
This understanding is crucial for the subsequent evaluation of the long-term effects of commercially prepared infant food on child development.
1. Convenience
The attribute of convenience, when applied to commercially prepared infant nourishment packaged in jars, directly addresses the constraints of time and resources faced by contemporary caregivers. It represents a paradigm shift from traditional methods of homemade food preparation for infants.
- Reduced Preparation Time
The most salient aspect of convenience is the elimination of time-intensive processes associated with preparing infant meals from raw ingredients. This includes sourcing, washing, peeling, cooking, and pureeing, all of which are bypassed through the use of prepared options. Caregivers can therefore allocate their time to other essential childcare duties or personal obligations.
- Portability and Ease of Use
Sealed containers offer inherent portability, allowing for easy transportation and feeding in diverse settings, such as daycare facilities, travel environments, or social gatherings. The pre-portioned nature of most offerings further simplifies meal planning and reduces waste. No additional equipment beyond a feeding utensil is typically required.
- Extended Shelf Life
Modern preservation techniques, such as pasteurization and vacuum sealing, extend the shelf life of these products significantly compared to fresh, homemade alternatives. This extended shelf life enables caregivers to maintain a readily available supply of infant meals without the need for frequent shopping trips or concerns about spoilage.
- Standardized Nutritional Content
Manufacturers are required to adhere to nutritional guidelines, ensuring a consistent nutrient profile across batches. This standardization provides caregivers with a degree of assurance regarding the nutritional adequacy of the infant’s diet, especially when compared to the variability potentially encountered in homemade preparations. Precise nutritional information is easily accessible on product labels.
These facets of convenience, while not the sole determinants of infant feeding choices, exert a considerable influence on caregivers seeking efficient and reliable solutions for meeting their child’s nutritional requirements. The availability and widespread adoption of prepared infant nourishment packaged in jars reflect the increasing value placed on time-saving and practical solutions in modern childcare practices.
2. Nutritional Content
The nutritional content of infant nourishment presented in jars represents a critical factor in infant health and development. The composition of these products directly influences growth, cognitive development, and the establishment of healthy eating habits. Manufacturers formulate these meals to meet specific nutritional guidelines established by regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration, ensuring adequate levels of essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients. For example, iron-fortified options address the high iron requirements of infants, preventing iron-deficiency anemia. Similarly, appropriate levels of vitamin D are incorporated to support bone health and calcium absorption.
The nutritional profiles of jarred infant meals can vary significantly depending on the ingredients and processing methods employed. Single-ingredient purees, such as sweet potato or apple sauce, provide focused sources of specific nutrients, while multi-ingredient blends offer a more complex nutritional matrix. The processing techniques, including heating and preservation methods, can impact the bioavailability of certain nutrients. For instance, excessive heating may reduce the levels of heat-sensitive vitamins. Careful monitoring of nutrient levels throughout the manufacturing process is therefore paramount. Furthermore, the presence of additives, such as added sugars or salts, can detract from the overall nutritional value and potentially contribute to unhealthy dietary habits. Consequently, a thorough review of product labeling is essential for informed decision-making.
In summary, the nutritional content of jarred infant nourishment is a critical determinant of its suitability for infant feeding. Adherence to established nutritional guidelines, careful selection of ingredients, and appropriate processing methods are essential for ensuring optimal infant health and development. Caregivers should carefully evaluate product labels and consider the specific nutritional needs of their child when selecting commercially prepared infant meals. The ongoing monitoring and assessment of nutritional content remain crucial for ensuring that these products effectively support infant well-being.
3. Ingredient Transparency
Ingredient transparency, in the context of commercially prepared infant nourishment, refers to the clear and accessible presentation of the components used in the production of these items. This facet is paramount for informed consumer decision-making and contributes directly to the perceived trustworthiness and safety of the product.
- Clear Labeling Requirements
Regulatory bodies mandate specific labeling requirements for infant nourishment. These regulations dictate the precise listing of all ingredients in descending order by weight, along with nutritional information. These requirements provide a baseline level of transparency, enabling caregivers to identify potential allergens or unwanted additives. For instance, a label must clearly state if a product contains common allergens like milk, soy, or wheat.
- Absence of Ambiguous Terms
True ingredient transparency necessitates the avoidance of vague or ambiguous terms on product labels. Instead of using catch-all phrases like “natural flavors,” manufacturers should explicitly list the specific flavoring agents used. Similarly, the source of fats and oils should be clearly identified, allowing caregivers to make informed choices based on their dietary preferences and concerns.
- Disclosure of Processing Aids
Beyond the list of ingredients that remain in the final product, transparency extends to the disclosure of processing aids used during manufacturing. Although these substances may not be present in the final product, their use can be relevant for individuals with sensitivities or ethical concerns. For example, the use of certain enzymes or clarifying agents could be pertinent information for some consumers.
- Traceability of Ingredients
The highest level of ingredient transparency involves the ability to trace the origin of each component used in the infant nourishment. This includes information about the source of the ingredients, farming practices, and the manufacturing processes employed. Such traceability can enhance consumer confidence and facilitate accountability within the supply chain.
The degree of ingredient transparency directly impacts a caregiver’s ability to assess the suitability of commercially prepared infant meals for their child. Comprehensive and unambiguous labeling, coupled with traceability initiatives, empowers consumers to make informed choices that align with their individual values and dietary requirements. Increased transparency fosters trust and promotes responsible manufacturing practices within the industry.
4. Safety Standards
The safety standards governing the production of infant nourishment packaged in jars are paramount in ensuring the health and well-being of the consumer. These standards encompass a range of stringent regulations and practices designed to minimize the risk of contamination, ensure nutritional adequacy, and prevent the introduction of harmful substances. The integrity of these standards is fundamental to maintaining consumer trust and protecting vulnerable populations.
- Material Safety and Jar Integrity
The materials used in the manufacture of the containers are subject to strict regulations. The glass must be food-grade and free from contaminants. Sealing mechanisms undergo rigorous testing to ensure airtight closure, preventing microbial contamination and maintaining product freshness. Jar integrity testing includes impact resistance and thermal shock assessments, simulating potential stresses encountered during transportation and storage. Any breach in the container compromises product safety.
- Sterilization and Pasteurization Processes
Commercially prepared infant foods undergo sterilization or pasteurization processes to eliminate harmful bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. Sterilization involves heating the product to a high temperature to kill all viable microorganisms, while pasteurization reduces the number of harmful microorganisms to a safe level. Both processes are carefully controlled to prevent nutrient degradation and maintain product quality. Regular validation of these processes is essential to ensure effectiveness.
- Contaminant Monitoring and Residue Limits
Stringent monitoring programs are implemented to detect and control potential contaminants, including heavy metals, pesticides, and toxins. Maximum residue limits (MRLs) are established for various substances to ensure that levels remain below acceptable thresholds. Regular testing of raw materials and finished products is conducted to verify compliance with these limits. Failure to meet these standards results in product rejection or recall.
- Manufacturing Facility Hygiene and Sanitation
Production facilities must adhere to strict hygiene and sanitation protocols. These include regular cleaning and disinfection of equipment, implementation of pest control programs, and proper waste management practices. Personnel are required to follow strict hygiene procedures, including handwashing and wearing protective clothing. Regular audits and inspections are conducted to ensure compliance with these standards.
These safety standards, collectively, constitute a comprehensive framework for ensuring the safety and quality of commercially prepared infant nourishment packaged in jars. Adherence to these standards is not merely a legal requirement but a moral imperative, safeguarding the health and well-being of infants. Continuous monitoring, improvement, and adaptation of these standards are essential to address emerging challenges and maintain consumer confidence.
5. Storage Requirements
The storage requirements for infant comestibles packaged in jars constitute a critical component of ensuring product safety and maintaining nutritional integrity throughout the shelf life. Adherence to specified storage guidelines minimizes the risk of spoilage, bacterial contamination, and nutrient degradation, thereby safeguarding the health of the infant consumer.
- Unopened Jar Storage
Unopened commercially prepared infant nourishment should be stored in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations. Elevated temperatures can accelerate nutrient degradation and potentially compromise the integrity of the packaging. Optimal storage temperatures typically range from 10C to 25C (50F to 77F). Exposure to direct sunlight can similarly degrade vitamins and other light-sensitive nutrients. Adherence to these conditions maximizes shelf life and preserves product quality. For example, storing jars near a stove or in a hot car can significantly reduce their shelf life and increase the risk of spoilage.
- Refrigeration After Opening
Once opened, jars of infant nourishment require immediate refrigeration to inhibit bacterial growth. The introduction of a feeding utensil into the jar introduces potential contaminants, necessitating prompt refrigeration. The recommended refrigeration temperature is typically between 2C and 4C (36F and 40F). Opened jars should be tightly sealed or covered to prevent the absorption of odors and maintain moisture levels. Failure to refrigerate opened jars within the recommended timeframe increases the risk of foodborne illness. Discarding any unused portion after a specified period, typically 24-48 hours, is also essential.
- Freezing Considerations
While freezing can extend the shelf life of commercially prepared infant nourishment, it is not universally recommended due to potential texture and flavor alterations. Freezing can cause separation of ingredients and changes in consistency, which may affect palatability. If freezing is elected, the contents should be transferred to a freezer-safe container with minimal headspace to prevent freezer burn. Thawing should be conducted in the refrigerator, not at room temperature, to minimize bacterial growth. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial before freezing infant meals packaged in jars.
- Visual Inspection and Discard Protocol
Prior to each use, a thorough visual inspection of the contents is imperative, even within the recommended storage period. Any signs of spoilage, such as discoloration, unusual odors, or changes in texture, indicate product deterioration. Bulging lids or compromised seals suggest potential contamination and warrant immediate disposal. Adherence to a strict discard protocol, regardless of whether the expiration date has been reached, is a critical safety measure.
These storage guidelines are integral to maintaining the safety and nutritional value of commercially prepared infant comestibles presented in jars. The conscientious application of these practices by caregivers mitigates potential health risks and ensures that the infant receives a safe and nutritious food product. The continued adherence to recommended storage protocols remains a cornerstone of responsible infant feeding practices.
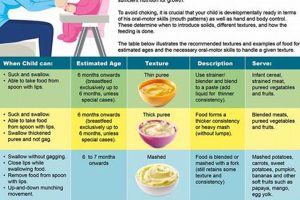
6. Stage Appropriateness
Stage appropriateness is a critical consideration in the context of commercially prepared infant comestibles. It ensures that the texture, nutritional composition, and ingredient complexity of these products align with the developmental capabilities and nutritional requirements of infants at different stages of growth. Failure to adhere to stage-appropriate formulations can lead to digestive distress, inadequate nutrient intake, or the introduction of allergens prematurely.
- Texture Progression and Swallowing Ability
Infants progress through distinct stages of oral motor development, necessitating corresponding adjustments in food texture. Early stages typically require smooth purees to accommodate limited swallowing abilities and prevent choking hazards. As infants develop, textures can gradually advance to include thicker consistencies, mashed foods, and eventually, small, soft pieces. Manufacturers categorize products according to these stages, providing clear guidance for caregivers. Introducing textures that are too advanced can result in gagging, choking, or food refusal. For example, a Stage 1 product will be a smooth puree of a single fruit or vegetable, while a Stage 3 product might contain small, soft pieces of multiple ingredients.
- Nutritional Requirements and Age-Specific Formulations
Nutritional needs vary significantly throughout infancy. Early stages focus on easily digestible nutrients and minimal allergenic potential. Later stages require increased caloric density and a broader range of vitamins and minerals to support rapid growth and development. Commercially prepared infant nourishment is formulated to meet these age-specific nutritional requirements, with variations in macronutrient ratios (protein, fat, carbohydrates) and micronutrient fortification. For example, products designed for infants over six months often include added iron to address the depletion of iron stores after birth.
- Ingredient Introduction and Allergen Awareness
The introduction of new ingredients should be gradual and systematic to facilitate the identification of potential allergens. Stage-appropriate products typically begin with single-ingredient purees of low-allergen foods, such as sweet potatoes or pears. As infants demonstrate tolerance, more complex combinations and potentially allergenic ingredients, such as dairy or soy, can be introduced cautiously. Clear labeling and ingredient transparency are essential for caregivers to monitor for adverse reactions. Delaying the introduction of solid foods beyond six months and the specific introduction sequence is associated with an increase risk of allergies.
- Digestive Maturity and Food Tolerance
The digestive system of an infant matures progressively, impacting the ability to process different types of foods. Early stages require easily digestible options with minimal fiber content. As the digestive system develops, infants can tolerate more complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Stage-appropriate formulations consider these digestive limitations, avoiding ingredients that may cause gas, bloating, or diarrhea. For example, legume-based products are typically introduced at later stages to allow for improved digestive capacity.
These facets underscore the importance of selecting commercially prepared infant nourishment that aligns with the infant’s developmental stage. Thoughtful consideration of texture, nutritional needs, ingredient introduction, and digestive maturity is essential for promoting optimal health and minimizing potential risks. The detailed labeling and stage categorization of these products assist caregivers in making informed choices that support the infant’s growth and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding commercially prepared infant meals. Information provided herein is intended to offer clarification and guidance on informed usage.
Question 1: What are the primary benefits of utilizing commercially prepared infant food?
Pre-packaged infant nourishment offers convenience, standardization of nutritional content, and extended shelf life compared to homemade alternatives. These factors can be particularly beneficial for caregivers with time constraints or those seeking assurance regarding nutritional adequacy.
Question 2: Are commercially prepared infant foods nutritionally equivalent to homemade options?
When manufactured according to established nutritional guidelines, commercially prepared infant nourishment can provide comparable nutritional value to homemade options. However, the specific nutrient content depends on the ingredients and processing methods employed. Careful review of product labeling is essential.
Question 3: How should opened containers of commercially prepared infant food be stored?
Opened containers require immediate refrigeration to inhibit bacterial growth. The recommended refrigeration temperature is between 2C and 4C (36F and 40F). Unused portions should be discarded after 24 to 48 hours to minimize the risk of foodborne illness.
Question 4: What precautions should be taken when introducing new varieties of commercially prepared infant nourishment?
New varieties should be introduced one at a time, allowing several days between each introduction, to effectively monitor for potential allergic reactions or sensitivities. Starting with single-ingredient purees of low-allergen foods is recommended.
Question 5: Are there concerns regarding potential contaminants in commercially prepared infant foods?
Manufacturers are required to adhere to stringent safety standards and monitoring programs to minimize the risk of contaminants, including heavy metals and pesticides. However, independent testing and advocacy groups continue to monitor for potential issues. Selecting products from reputable brands and carefully reviewing product information can mitigate these concerns.
Question 6: Is heating commercially prepared infant nourishment necessary? If so, what is the recommended method?
Heating is not essential, but some caregivers prefer to warm the product. If warming is desired, the contents should be transferred to a microwave-safe dish and heated evenly to prevent hot spots. Avoid microwaving in the container. Always test the temperature before feeding.
These FAQs are intended to offer clarity regarding commonly encountered concerns or misconceptions surrounding pre-packaged infant meals. Careful consideration of these points contributes to informed and responsible feeding practices.
The subsequent section will delve into potential future trends and emerging research related to infant nutritional practices.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has illuminated the multifaceted aspects of commercially prepared infant nourishment. Key considerations include convenience, nutritional content, ingredient transparency, adherence to rigorous safety standards, appropriate storage protocols, and stage-specific formulations. These factors collectively influence the suitability of such products for infant feeding and necessitate informed decision-making by caregivers.
The ongoing evolution of manufacturing processes, coupled with continued research into infant nutritional needs, holds the potential to further enhance the safety, quality, and suitability of these products. Vigilant monitoring of regulatory compliance, coupled with proactive engagement by healthcare professionals, remains crucial in ensuring optimal outcomes for infant health and development. “Jars of baby food” represent a significant component of modern infant feeding practices, demanding continued scrutiny and responsible utilization.