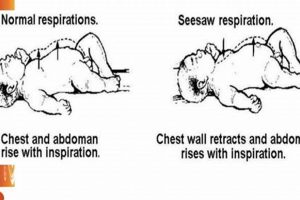
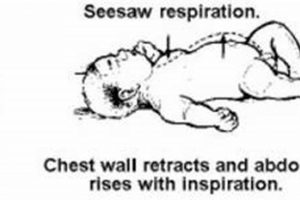
Paradoxical respiration in infants, characterized by the chest retracting inward while the abdomen expands during inhalation and the chest expanding outward as the abdomen moves inward during exhalation, indicates significant respiratory distress.... Read more »
Diaphragmatic breathing, observed in infants, involves the expansion of the abdomen during inhalation and its contraction during exhalation. This breathing pattern is characterized by minimal chest movement, with the primary action originating... Read more »

Infant respiration is characterized by the prominent movement of the abdominal area during inhalation and exhalation. This visible rise and fall of the abdomen, rather than the chest, is a typical pattern... Read more »


