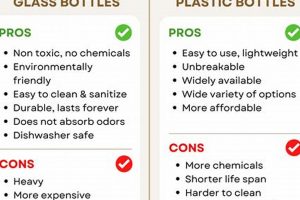
The question of whether infant feeding containers are suitable for cleaning within an automated dishwashing appliance is a common inquiry among caregivers. This method of sanitation offers convenience, but understanding the properties of the bottle materials and the capabilities of the dishwasher is essential. Considerations include the bottle’s construction (plastic, glass, or other material), the temperature reached within the dishwasher, and the potential for chemical residue from detergents.
Utilizing an automated dishwashing appliance for cleaning feeding containers provides benefits such as thorough sanitation through high temperatures and the elimination of manual scrubbing, potentially reducing the risk of bacterial contamination. Historically, sterilization methods involved boiling; modern dishwashers can offer a similar level of cleanliness when used correctly. However, improper use or incompatible materials may lead to degradation of the bottle or introduction of harmful chemicals.
Therefore, the following sections will delve into specific considerations regarding material compatibility, appropriate dishwasher settings, recommended detergents, and best practices to ensure the safe and effective sanitation of infant feeding containers within a dishwashing appliance. Proper execution ensures both cleanliness and the longevity of the bottles.
Dishwasher Sanitation Guidelines for Infant Feeding Containers
The following recommendations provide guidance on effectively and safely sanitizing infant feeding containers using an automated dishwashing appliance, minimizing potential risks associated with material degradation and chemical contamination.
Tip 1: Material Compatibility Assessment: Prior to introducing any feeding container to the dishwasher, verify its compatibility with high-temperature environments. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines, typically found on the packaging or the manufacturer’s website. Polypropylene (PP) bottles are generally considered dishwasher-safe, while some older polycarbonate (PC) bottles may leach Bisphenol A (BPA) under high heat.
Tip 2: Utilize the Upper Rack: Placement on the upper rack minimizes exposure to the heating element, mitigating the risk of warping or melting. This is particularly crucial for plastic components such as bottle nipples and sealing rings. Ensure items are secured to prevent them from falling onto the heating element during the wash cycle.
Tip 3: Select Appropriate Dishwasher Settings: Opt for a cycle with moderate temperatures, ideally between 140F (60C) and 150F (66C). Avoid high-temperature sanitizing cycles or prolonged drying cycles, as these may accelerate material degradation. Consider a dedicated bottle washing cycle if the appliance offers one.
Tip 4: Detergent Selection: Employ a mild, fragrance-free detergent specifically formulated for baby items or sensitive individuals. Thoroughly rinse all components after washing to eliminate any residual detergent, which could potentially irritate the infant or alter the taste of the formula or breast milk.
Tip 5: Pre-Washing Procedures: Before loading, remove any excess formula or milk residue from the bottles and nipples. A thorough rinse under running water with a dedicated bottle brush can significantly improve the dishwasher’s efficacy in removing stubborn stains and preventing the accumulation of bacteria.
Tip 6: Inspection Post-Cycle: Following each wash cycle, carefully inspect the bottles and nipples for any signs of damage, such as cracks, discoloration, or warping. Discard any compromised items immediately to prevent potential hazards.
Tip 7: Storage Considerations: Once thoroughly dry, store the sanitized bottles and nipples in a clean, airtight container or bag to prevent contamination from airborne particles. Avoid storing in damp or humid environments, which can promote bacterial growth.
Adherence to these guidelines ensures a more effective and safer approach to sanitizing infant feeding containers within a dishwashing appliance, ultimately contributing to the health and well-being of the infant.
The subsequent section will address alternative sanitation methods and further precautions for specific bottle types.
1. Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is a primary determinant in assessing whether infant feeding containers can be safely and effectively cleaned within a dishwasher. The chemical and physical properties of the bottle’s constituent materials dictate its resistance to the dishwasher’s environment, including high temperatures and chemical exposure.
- Plastic Polymer Composition
The type of plastic used significantly impacts dishwasher suitability. Polypropylene (PP) is generally accepted as dishwasher-safe due to its high melting point and chemical resistance. Conversely, older polycarbonate (PC) bottles, which may contain Bisphenol A (BPA), are less suitable due to potential BPA leaching under high heat and degradation of the plastic. Checking manufacturer’s guidelines is paramount to ascertain the specific plastic type and its recommended cleaning methods.
- Glass Composition and Tempering
Glass bottles are often considered dishwasher-safe, but the composition and tempering process influence their durability. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal shock resistance, is less prone to shattering during temperature fluctuations within the dishwasher. However, even tempered glass can crack or chip if subjected to extreme temperature changes or physical impact. Careful handling and placement within the dishwasher are necessary.
- Nipple and Component Materials
Bottle nipples and other small components, frequently made from silicone or rubber, also require material compatibility assessment. Silicone is generally dishwasher-safe, but prolonged exposure to high heat and harsh detergents can degrade its elasticity and integrity. Rubber components are more susceptible to damage and may become brittle or leach chemicals. These components often require upper rack placement or hand washing to extend their lifespan.
- Chemical Resistance
The dishwasher’s detergent solutions can impact bottle materials. Harsh detergents containing strong alkalis or chlorine bleach can degrade certain plastics and cause discoloration or cracking. Residue from these detergents can also pose a health risk to the infant. Choosing a mild, fragrance-free detergent specifically formulated for baby items minimizes the risk of chemical damage and residue contamination.
Understanding the material composition of infant feeding containers is essential for making informed decisions about dishwasher use. Prioritizing material compatibility ensures both effective sanitation and prevents the introduction of harmful chemicals or degraded materials to the infant’s feeding process. Ignoring material specifications can lead to bottle damage, potential health hazards, and negate any convenience gains.
2. Upper Rack Placement
The position of infant feeding containers within a dishwasher during the cleaning cycle, specifically upper rack placement, significantly influences the outcome of the sanitation process. Correct positioning is essential to mitigate potential damage and ensure effective cleaning, thus directly impacting the determination of suitability for dishwasher use.
- Reduced Heat Exposure
The upper rack generally experiences lower temperatures compared to the lower rack, where the heating element is typically located. Direct exposure to high heat can warp, melt, or degrade plastic components of baby bottles, particularly those made from less heat-resistant polymers. Upper rack placement minimizes this risk, preserving the integrity of the bottles.
- Prevention of Direct Spray Impingement
The lower rack often receives more forceful water spray from the dishwasher’s rotating arms. Direct impingement can cause smaller items like nipples and bottle components to dislodge and potentially fall onto the heating element or become trapped in the dishwasher’s mechanism. The upper rack provides a more sheltered environment, reducing the likelihood of such incidents.
- Mitigation of Chemical Detergent Concentration
While the dishwasher aims to distribute detergent evenly, localized concentrations can occur. The upper rack may experience less direct exposure to concentrated detergent streams, reducing the potential for chemical residue to cling to bottle surfaces. This is especially important when using detergents that may not be specifically formulated for infant items, as residue can pose a risk.
- Improved Air Circulation for Drying
The upper rack often benefits from better air circulation during the drying cycle, facilitating more complete evaporation of moisture. Residual moisture can promote bacterial growth, negating the sanitation benefits of the wash cycle. Proper air circulation in the upper rack helps to ensure that bottles are thoroughly dried and ready for storage, further supporting the cleanliness objective.
In conclusion, strategic positioning of infant feeding containers on the upper rack of a dishwasher is not merely a matter of convenience; it represents a crucial step in safeguarding the physical integrity of the bottles and minimizing potential health risks. By reducing heat exposure, preventing direct spray impingement, mitigating chemical concentration, and enhancing air circulation, upper rack placement contributes significantly to the safe and effective dishwasher sanitation of infant feeding equipment.
3. Temperature Settings
The selection of appropriate temperature settings is a pivotal factor when determining the suitability of dishwashing appliances for cleaning infant feeding containers. The temperatures reached during various dishwasher cycles directly influence the structural integrity of the bottles and the effectiveness of the sanitation process. Elevated temperatures are necessary to eliminate harmful bacteria, but excessive heat can compromise the materials, leading to warping, cracking, or the leaching of chemicals.
High-temperature sanitization cycles, often exceeding 160F (71C), while effective for killing pathogens, may be detrimental to certain types of plastic bottles, particularly those not explicitly labeled as dishwasher-safe. The sustained exposure to high heat can cause plastic polymers to degrade, potentially releasing harmful substances into the container. Conversely, lower temperature cycles may not provide adequate sanitation, leaving residual bacteria on the bottle’s surface. A balance must be struck, typically opting for a moderate temperature setting, around 140F (60C), combined with a reputable detergent to achieve both cleanliness and material preservation. For example, some caregivers choose a “delicate” or “glassware” cycle, which usually uses lower temperatures and gentler water pressure.
Therefore, consulting the manufacturer’s instructions for both the infant feeding containers and the dishwasher is essential. These guidelines provide specific temperature recommendations that optimize sanitation while minimizing the risk of damage. Ignoring these recommendations can lead to premature degradation of the bottles, rendering them unsafe for use. Careful consideration of temperature settings, coupled with appropriate bottle placement and detergent selection, is crucial for safely and effectively utilizing dishwashers to clean infant feeding containers.
4. Detergent Type
The selection of an appropriate detergent type directly influences the suitability of dishwashing appliances for sanitizing infant feeding containers. Detergent composition can impact both the cleanliness and the material integrity of the bottles, making it a crucial factor to consider.
- Harsh Chemicals and Material Degradation
Conventional dishwashing detergents often contain harsh chemicals such as phosphates, chlorine bleach, and strong surfactants. These substances can degrade plastic polymers used in baby bottles, causing them to become brittle, cracked, or discolored. Leaching of potentially harmful chemicals from the plastic into the bottle’s contents is also a concern. Choosing detergents specifically formulated for baby items or sensitive individuals mitigates this risk.
- Residue and Infant Health
Even after rinsing, detergent residue can remain on the surface of bottles and nipples. Infants are particularly susceptible to the harmful effects of these residues due to their developing immune systems and lower body weight. Residues can cause irritation, allergic reactions, or digestive upset. Fragrance-free and dye-free detergents, which minimize the presence of potentially irritating compounds, are preferable.
- Enzyme-Based Cleaners and Organic Matter Removal
Enzyme-based detergents offer an alternative approach to cleaning by breaking down organic matter such as milk proteins and fats. These detergents are generally milder than conventional options and may be effective at removing residue without causing material damage. However, ensuring complete rinsing is still essential to prevent any potential enzyme residue from affecting the infant.
- Impact on Silicone and Rubber Components
Nipples and other bottle components made from silicone or rubber are particularly vulnerable to harsh detergents. These materials can absorb chemicals, leading to degradation and potential leaching. Mild detergents specifically designed for baby items help to preserve the integrity and longevity of these components.
In summary, the selection of a detergent must prioritize both effective cleaning and the health and safety of the infant. Mild, fragrance-free, and residue-free detergents are best suited for washing baby bottles in a dishwasher. Caregivers should diligently review detergent ingredients and prioritize options explicitly designed for infant use to minimize potential risks.
5. Pre-Washing Needed
The necessity of pre-washing infant feeding containers directly influences the efficacy and safety of utilizing dishwashing appliances for their sanitation. Dishwashers are designed to remove loosened debris and sanitize surfaces, but are not optimized to dislodge and eliminate caked-on milk residue or formula. Failure to pre-wash can lead to inadequate cleaning, leaving behind breeding grounds for bacteria, effectively negating the benefits of dishwasher sanitation. For instance, thick formula residue can shield microorganisms from the dishwasher’s spray and heat, preventing complete sterilization.
Pre-washing serves several critical functions. First, it physically removes the bulk of organic matter, allowing the dishwasher’s detergent and high temperatures to effectively target remaining microorganisms. Second, it prevents clogging of the dishwasher’s spray arms and filtration system with large particles of dried milk. Third, it reduces the likelihood of residue buildup on the bottles, which can be difficult to remove and may harbor bacteria. A simple rinse with warm water and a dedicated bottle brush before placing the bottles in the dishwasher significantly enhances the overall cleanliness.
Therefore, pre-washing is not merely an optional step, but a fundamental requirement for the effective dishwasher sanitation of infant feeding containers. It addresses the limitations of the dishwasher’s cleaning capabilities and ensures that the bottles are properly prepared for thorough sanitization. Neglecting this step can compromise the entire process, potentially exposing the infant to harmful bacteria despite the use of a dishwasher. The benefits of automated cleaning are realized only when coupled with proper pre-washing protocols.
6. Post-Wash Inspection
Post-wash inspection is an indispensable step in the process of using dishwashing appliances for cleaning infant feeding containers. It provides a critical quality control mechanism that ensures both the cleanliness and structural integrity of the bottles, thereby directly influencing the safety and suitability of dishwasher use for this purpose.
- Identification of Material Degradation
Dishwasher cycles, involving high temperatures and potentially harsh detergents, can cause subtle degradation of plastic or silicone components. Post-wash inspection allows for the detection of cracks, warps, discoloration, or changes in texture that may not be immediately apparent. Early identification of such damage prevents the continued use of compromised bottles, mitigating the risk of chemical leaching or bacterial contamination. For example, a hairline crack in a plastic bottle may harbor bacteria even after dishwashing, necessitating its removal from service.
- Assessment of Cleaning Effectiveness
Dishwashers, while convenient, may not always remove all traces of milk or formula residue, especially in hard-to-reach areas. Post-wash inspection provides an opportunity to visually confirm the complete removal of residue and ensures that no areas remain potentially contaminated. For example, residue buildup around the nipple base or bottle threads may require manual cleaning or a change in detergent type.
- Detection of Detergent Residue
Even with thorough rinsing, some dishwashing detergents may leave behind a residual film on bottle surfaces. Post-wash inspection allows for the identification of this film, which can be harmful to infants if ingested. Running the bottles under water can sometimes reveal suds or a slippery texture, indicating the presence of detergent residue. If residue is detected, an additional rinse cycle or a change to a gentler detergent may be necessary.
- Verification of Component Integrity
Dishwasher cycles can dislodge or damage smaller components such as nipples, valves, or seals. Post-wash inspection allows for the confirmation that all components are present, properly assembled, and free from damage. A missing valve or a torn nipple can compromise the bottle’s functionality and potentially pose a choking hazard.
In conclusion, post-wash inspection serves as a vital safeguard when using dishwashers to clean infant feeding containers. By facilitating the detection of material degradation, assessing cleaning effectiveness, identifying detergent residue, and verifying component integrity, this process ensures that only clean, safe, and functional bottles are used for infant feeding. This rigorous inspection protocol is essential for mitigating potential health risks and ensuring the suitability of dishwashing as a safe method for bottle sanitation.
7. Storage After Cleaning
The effectiveness of utilizing a dishwasher to sanitize infant feeding containers is inextricably linked to the subsequent storage practices. Improper storage following a dishwasher cycle can negate the sanitation achieved, rendering the process ineffective and potentially harmful. While a dishwasher can eliminate microorganisms present on the bottles, the environment in which they are stored post-cleaning dictates whether those surfaces remain sanitary until their next use. For example, storing freshly sanitized bottles on a damp countertop allows for rapid re-colonization by bacteria, effectively undermining the dishwasher’s efforts.
Appropriate storage protocols following dishwasher sanitation are crucial for maintaining a sterile environment. Recommended practices include storing bottles in a clean, dry, and airtight container or bag. This protects the bottles from airborne contaminants and prevents moisture accumulation, which promotes microbial growth. Furthermore, ensuring that the bottles are completely dry before storage is essential, as residual moisture provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. An example of this would be inverting the bottles on a clean drying rack specifically designed for baby bottles to ensure complete air circulation. The selection of a storage location that is free from dust and potential contamination sources further enhances the overall sanitation process.
In conclusion, the suitability of dishwashing infant feeding containers hinges not only on the cleaning process itself but also on the subsequent storage methods. Effective sanitation is a two-part process: rigorous cleaning followed by meticulous storage. Failure to adhere to proper storage protocols following dishwashing undermines the sanitation efforts, potentially compromising the infant’s health. Therefore, implementing appropriate storage practices is an essential component of a comprehensive approach to infant feeding container hygiene and sanitation.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Dishwasher Use for Infant Feeding Containers
The following section addresses common inquiries concerning the suitability of dishwashing appliances for cleaning infant feeding containers. These answers are intended to provide clear and accurate information based on current best practices.
Question 1: Is it universally safe to clean all baby bottles in a dishwasher?
The safety depends primarily on the bottle’s material. Polypropylene (PP) bottles are generally dishwasher-safe, while older polycarbonate (PC) bottles may leach Bisphenol A (BPA) under high heat. Glass bottles are typically safe, but tempering and composition influence durability. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Question 2: What dishwasher settings are recommended for cleaning baby bottles?
A cycle with moderate temperatures, ideally between 140F (60C) and 150F (66C), is recommended. Avoid high-temperature sanitizing cycles or prolonged drying cycles, as these may accelerate material degradation. If available, a dedicated bottle washing cycle may be used.
Question 3: Are specific detergents preferred for cleaning baby bottles in a dishwasher?
A mild, fragrance-free detergent specifically formulated for baby items or sensitive individuals is preferred. Harsh chemicals and strong fragrances can leave residue and potentially harm the infant. Thorough rinsing is essential to remove any detergent traces.
Question 4: Is pre-washing necessary before placing baby bottles in the dishwasher?
Pre-washing, involving rinsing under running water and using a dedicated bottle brush, is strongly recommended. It removes excess formula or milk residue, improving the dishwasher’s efficacy in removing stubborn stains and preventing bacterial accumulation.
Question 5: What should be inspected on baby bottles after a dishwasher cycle?
Inspect for any signs of damage, such as cracks, discoloration, or warping. Discard any compromised items immediately to prevent potential hazards. Also, check for detergent residue, indicated by a slippery texture or suds.
Question 6: How should baby bottles be stored after cleaning in a dishwasher?
Store the sanitized bottles and nipples in a clean, airtight container or bag to prevent contamination from airborne particles. Ensure the bottles are completely dry before storage to prevent bacterial growth. Avoid storing in damp or humid environments.
These responses aim to provide a concise understanding of best practices for safely and effectively using dishwashers to clean infant feeding containers. Proper adherence to these guidelines is crucial for minimizing potential health risks.
The following section will summarize the key considerations and provide a final recommendation on dishwasher usage for baby bottles.
Can I Put Baby Bottles in the Dishwasher
The preceding analysis thoroughly examined the multifaceted considerations surrounding the practice of cleaning infant feeding containers in dishwashing appliances. Crucial determinants include material compatibility, optimal dishwasher settings, appropriate detergent selection, the necessity of pre-washing, diligent post-wash inspection, and proper storage protocols. Each of these elements plays a critical role in ensuring that the intended sanitation process is both effective and safe for infant use.
Given the potential for material degradation, chemical residue, and incomplete sanitation, diligent adherence to recommended guidelines is paramount. Caregivers are urged to prioritize infant safety by meticulously following manufacturer instructions and maintaining a vigilant approach to each step of the cleaning and storage process. While dishwashers can offer convenience, the ultimate responsibility for safeguarding infant health rests on informed and conscientious practices.